본문
[SageMaker] JumpStart로 Llama 3 모델 배포 및 추론하기
본 실습을 통해 SageMaker Studio의 손쉬운 배포기능 중 하나인 Jumpstart 모델을 활용하여 Llama3 모델을 배포해보고 이를 활용하여 추론을 진행하는 방법에 대해 습득할 수 있습니다.
1. SageMaker Studio 설정하기
1.1. SagMaker Studio 를 사용하기 위해 도메인을 생성하도록 하겠습니다.

빠른사용자 설정으로 진행하도록 하겠습니다.

잠시 후 구성이 완료됩니다.

1.2. 도메인이 생성되면 사용자를 생성합니다.
사용자 이름을 입력하고 다음으로 진행합니다.

기본적으로 Jumpstart 기능이 on 되어있으나, 확인 후 진행합니다.
RStudio는 사용하지 않으므로 그대로 진행합니다.
Canvas 기본 권한을 설정하는데, 실습에서는 다른 설정 없이 그대로 생성하도록 하겠습니다.

사용자 생성이 완료되면, Studio에 접속 할 수 있습니다.

2. Llama3 배포해보기
2.1. Studio에 접속하면, Jumpstart 메뉴를 확인할 수 있습니다.

2.2. Llama3 모델을 배포해보도록 하겠습니다.
검색기능을 활용하여 Llama3 8B 모델을 검색합니다. Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct 로 검색을 진행합니다

Meta는 AWS 모델 프로바이더 중 하나이며, 때문에 해당 모델을 쉽게 배포할 수 있습니다.
모델 스펙을 설정 후 진행합니다. 스케일링은 필요없으므로, 1개로 설정 후 배포하도록 하겠습니다.
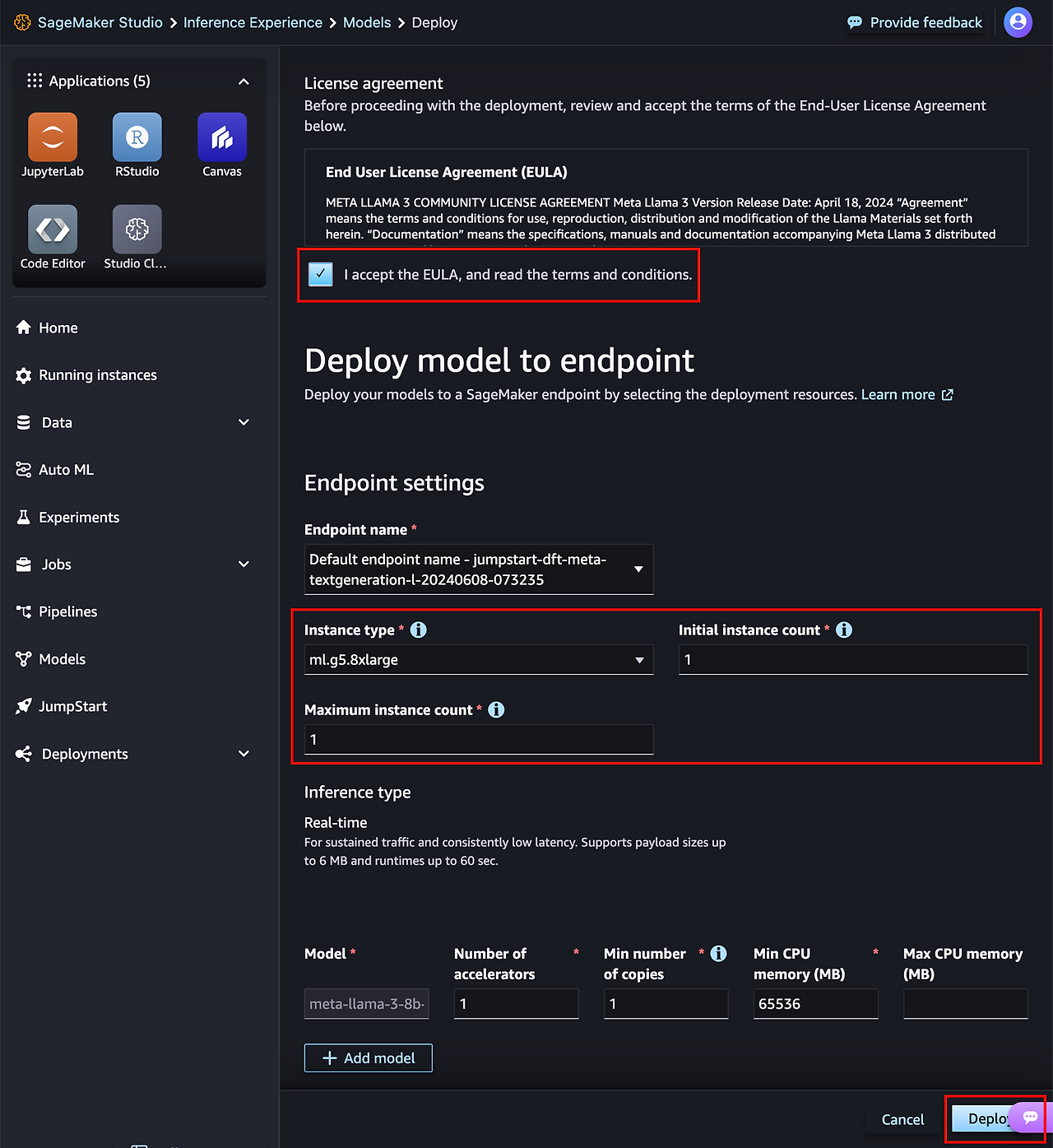
2.3. Inservice 가 확인되면 추론을 진행합니다.
Test Inference 탭에서 예제 코드를 제공합니다.
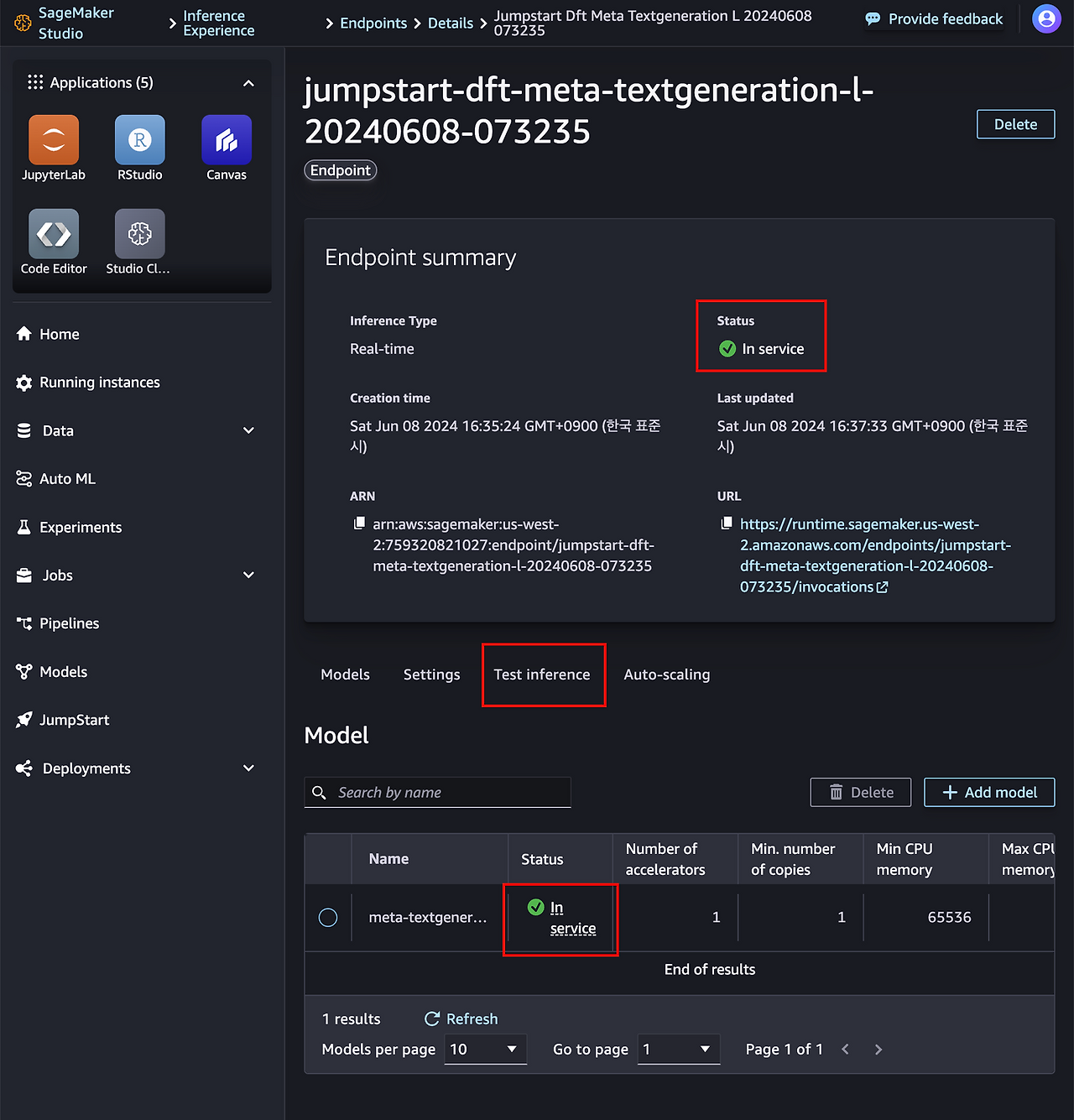
예제코드는 다음과 같습니다.
from sagemaker.predictor import retrieve_default
# 엔드포인트 이름 설정
endpoint_name = "jumpstart-dft-meta-textgeneration-l-20240608-073235"
# predictor 초기화. 이때 엔드포인트 이름과 추론 컴포넌트 이름 필요
predictor = retrieve_default(endpoint_name=endpoint_name, inference_component_name='meta-textgeneration-llama-3-8b-instruct-20240608-073238')
# 모델에 전송할 페이로드 설정
payload = {
"inputs": "<|begin_of_text|><|start_header_id|>user<|end_header_id|>\n\nwhat is the recipe of mayonnaise?<|eot_id|><|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>\n\n",
"parameters": {
"max_new_tokens": 256,
"top_p": 0.9,
"temperature": 0.6,
"stop": "<|eot_id|>"
}
}
# 응답 받아오기
response = predictor.predict(payload)
print(response)SageMaker SDK를 설치합니다.
!pip install sagemaker
예제코드를 원하는 리전으로 세션을 구성하고, 호출하는 방식으로 변경하였습니다.
import boto3
from sagemaker.predictor import retrieve_default
from sagemaker import Session
# 원하는 리전 설정
region_name = "us-west-2"
# 해당 리전으로 boto3 세션 생성
boto_session = boto3.Session(region_name=region_name)
# SageMaker 세션 생성
sagemaker_session = Session(boto_session=boto_session)
# 엔드포인트 이름 설정
endpoint_name = "jumpstart-dft-meta-textgeneration-l-20240608-073235"
# predictor 초기화. 이때 엔드포인트 이름과 추론 컴포넌트 이름 필요
predictor = retrieve_default(
endpoint_name=endpoint_name,
inference_component_name="meta-textgeneration-llama-3-8b-instruct-20240608-073238",
sagemaker_session=sagemaker_session,
)
# 모델에 전송할 페이로드 설정
payload = {
"inputs": "<|begin_of_text|><|start_header_id|>user<|end_header_id|>\n\nwhat is the recipe of mayonnaise?<|eot_id|><|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>\n\n",
"parameters": {
"max_new_tokens": 256,
"top_p": 0.9,
"temperature": 0.6,
"stop": "<|eot_id|>"
}
}
# 응답 받아오기
response = predictor.predict(payload)
print(response['generated_text'])
출력 결과는 다음과 같습니다.
The classic condiment! Mayonnaise is a thick, creamy sauce made from a combination of oil, egg yolks, acid (such as vinegar or lemon juice), and seasonings. Here's a simple recipe to make mayonnaise at home:
**Ingredients:**
* 2 egg yolks
* 1 tablespoon lemon juice or vinegar (such as apple cider vinegar or white wine vinegar)
* 1/2 teaspoon Dijon mustard (optional, but recommended for flavor)
* 1/2 cup (120 ml) neutral-tasting oil, such as canola, grapeseed, or sunflower oil
* Salt, to taste
* Water, as needed
**Instructions:**
1. **Start with room temperature ingredients**: Make sure your egg yolks, lemon juice, and oil are at room temperature. This will help the mixture emulsify smoothly.
2. **Whisk the egg yolks**: In a medium-sized bowl, whisk together the egg yolks and lemon juice until well combined.
3. **Add the mustard (if using)**: Whisk in the Dijon mustard, if using.
4. **Slowly add the oil**: While continuously whisking the egg yolk mixture, slowly pour in the oil
해당 코드를 통합하면, 애플리케이션에서 LLM을 호출하는 로직을 추가할 수 있습니다.
2.4. 리소스 제거
LLM을 호스팅하는 리소스는 GPU인스턴스를 사용하므로, 시간당 과금이 높은편이기때문에 필요하지 않은경우 엔드포인트를 반드시 제거해야합니다.





댓글