본문
Composite Pattern
파일 데이터와 같은 일반적인 트리 구조의 데이터 타입을 만드는 패턴
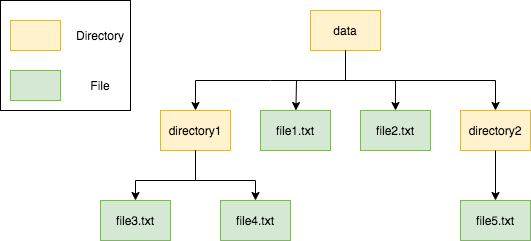
Composite 패턴에서 주요등장 인물은 3개입니다.
첫째는 상위 컴포넌트
둘째는 상위 컴포넌트를 상속 받으며 자식 컴포넌트를 가질 수 있는 Composite
셋째는 상위 컴포넌트를 상속 받으며, 하위 컴포넌트를 가질 수 없는 Leaf
디렉토리가 Composite라면, 파일은 Leaf라고 보시면 됩니다.
💡 Component.java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public abstract class Component {
private String componentName;
protected List<Component> children = new ArrayList<Component>();
public Component(String componentName) {
this.componentName = componentName;
}
public String getComponentName() {
return componentName;
}
public abstract void add(Component c);
public List<Component> getChildren() {
return children;
}
public String getString() {
return getString(0);
}
private String getString(int depth) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
if (this instanceof Composite) {
for (int i = 0; i < depth; i++) {
sb.append(" ");
}
sb.append("+" + getComponentName() + "\n");
for (Component comp : children) {
sb.append(comp.getString(depth + 1));
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < depth; i++) {
sb.append(" ");
}
sb.append("-" + getComponentName() + "\n");
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
💡 Composite.java
// 하위 Composite (하위 노드 가질 수 있음)
public class Composite
public Composite(String componentName) {
super(componentName);
}
@Override
public void add(Component c) {
}
}
💡 Leaf.java
// 하위 Leaf (하위 노드 가질 수 없음)
public class Leaf extends Component {
public Leaf(String componentName) {
super(componentName);
}
@Override
public void add(Component c) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
💡 Main.java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Composite main = new Composite("Main");
Composite sub1 = new Composite("sub1");
Composite sub2 = new Composite("sub2");
Composite sub11 = new Composite("sub11");
Composite sub12 = new Composite("sub12");
Composite sub13 = new Composite("sub13");
Composite sub21 = new Composite("sub21");
Composite sub22 = new Composite("sub22");
Leaf leaf14 = new Leaf("leaf14");
Leaf leaf121 = new Leaf("leaf121");
main.add(sub1);
main.add(sub2);
sub1.add(sub11);
sub1.add(sub12);
sub1.add(sub13);
sub2.add(sub21);
sub2.add(sub22);
sub1.add(leaf14);
sub12.add(leaf121);
System.out.println(main.getString());
}
}
💡 결과
+Main
+sub1
+sub11
+sub12
-leaf121
+sub13
-leaf14
+sub2
+sub21
+sub22
💡 트리 구조 구현
Component는 멤버 변수로 List<Component>를 가집니다. Component에 있어서 중요한 메소드는 add()와 getChildren()입니다. add()의 인자는 Component 이고, getChildren()의 리턴 타입도 List<Component>입니다. Composite인지 Leaf인지 구분하지 않습니다.
💡 add와 getChildren 구현
첫째, Component 에서 모든 것을 구현하고, Leaf에서는 add 메소드 호출 시 UnsupportedOperationException 을 던집니다.
둘째, Component 에서는 abstract로 선언만 하고 Composite와 Leaf에서 구현을 합니다. Leaf에서는 첫번째 방법과 마찬가지로 UnsupportedOperationException 를 던지면 됩니다. 구조는 복잡하지만, 첫번째 방법에 비해 다른 기능 추가는 상대적으로 쉽습니다.




댓글